Contact us
First Floor, 159 Victoria Pde
Collingwood, VIC 3066
(Google Map)
1300 727 952
or
+61 3 9910 4099
How to publish and open your dataset
Find out what open data is, why it’s good for Australia, and how to open your datasets using the open source data tool CKAN.
An introduction to open data
Open data has become an important part of the open government movement informing policy, providing greater transparency and encouraging co-production with citizens. In fact, government policy is that data should be ‘open by default’.
Below is some more information on open data, including what it is, why you should open your data and some of the work that’s already being done with open data. You can also go straight to our step-by-step guide to opening your data at How to open and publish your data.
What is open data?
Open data makes data available to the public (and businesses) to use and reuse as they wish. It should be available for free, and on an ongoing basis.
Why open your data?
There are two main reasons why you should open your data:
-
It’s government policy and a key part of one of the government’s 15 commitments in the Open Government National Plan (2.1 ‘Release high-value datasets and enable data driven innovation’).
-
Open data can be used to create apps and websites that deliver social and/or economic value.
Open and usable
One of the key elements of opening data, is to open it in a way that the data can be easily used. For example, while information that’s publicly available via PDFs is officially ‘open’ (because it’s publicly available), it’s not in a very usable form. Ideally, data should be machine-readable. CKAN is an ideal data tool.
Who’s already opened their datasets?
There are already many, many agencies that have opened their data. At the federal level, data.gov.au currently has nearly 29,000 discoverable datasets. Some of the agencies who own this data include:
- GeoScience Australia
- CSIRO
- Australian Antarctic Division
- Royal Australian Navy
- Department of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry
- Australian Bureau of Statistics
- Bureau of Meteorology
Likewise, many agencies at both the state and local levels have opened their datasets, making them publicly available on the relevant state website and data.gov.au.
Open data in action
GovHack is a great example of how open data can be used to deliver useful tools (apps and websites) to the broader community. Past winners provide an insight into theprojects born from open data. Examples include:
-
Community Report by Here For Bread (VIC) – a mobile app that allows people to log issues to their local council (view on Hackerspace).
-
The Health Craft by High Flyers (QLD) – finds suitable trial healthcare sites using data from patients who receive in-home care, can’t drive, are outside of normal public transport routes and require regular home care and healthcare products (view on Hackerspace).
-
Little Play Space by Little Play Space (NSW) – decreases social isolation in the elderly by matching past carers with children in need of care (view on Hackerspace).
-
Emergency Department Load Forecasting by Beast Mode (QLD) – uses data to estimate the daily ‘load’ in hospital emergency departments (like a weather forecast but a patient forecast) (view on Hackerspace).
-
SunSpot by Hackunamatata (SA) – identifies solar panels using satellite images so governments can identify solar status and provide intelligence about solar clusters by postcode or street (view on Hackerspace).
The CSIRO is also leading the open data charge, with its Data61 research project. The National Map is a Data61 project that plots a huge variety of data across a map of Australia — from native vegetation and caves, to bridges, road crashes and local council boundaries.
CKAN
CKAN is an open source data management tool that allows you to manage and publish data, delivering tangible benefits to citizens. It’s currently being used by big open data players such as data.gov, data.gov.uk and data.gov.au.
CKAN is a powerful tool for data custodians, because it allows you to not only manage data, but to display it as maps, tables or graphs. CKAN also includes a faceted search and data preview capabilities...all available for free as part of the open source movement.
Data.vic.gov.au is built using CKAN (a Salsa project and one of the many reasons we love talking about open data and CKAN). You can find out more about CKAN on our CKAN page.
Data.vic.gov.au
For the state of Victoria, the Department of Premier and Cabinet (DPC) has created data.vic.gov.au, a common 'place and space’ where open datasets owned/managed by Victorian government agencies can be discovered and shared/reused. Data.vic.gov.au is built using the open source technology CKAN.
Data.vic.gov.au is essentially a data platform that hosts a public directory (repository) of discoverable open datasets.
-
The physical datasets themselves may be hosted on various other platforms and/or the preferred locations of each individual agency.
-
Datasets and formats can be as simple as raw .csv or .xls files or as sophisticated as CKAN (or alternative) data platform instances themselves.
Data.vic.gov.au enables agencies to make their datasets discoverable by exposing them (via metadata schema definitions).
How to open and publish your data using CKAN
The CKAN information asset register (IAR) is a ‘discovery tool’ that allows people to easily find a range of open datasets – on one website. To open your dataset, the first step is to set them up in CKAN.
Step 1: Login using your credentials to access the CKAN IAR.
Depending on your user role (admin, editor or member) you will have different access to the CKAN IAR.
Admin - Can add/edit and delete datasets, as well as manage organisation settings and members.
Editor - Can add and edit datasets, but can’t manage organisation members.
Member - Can view the organisation's private datasets, but can’t add new datasets.
Step 2: Select the Datasets link in the menu.
Step 3: Select 'Add Dataset' button.
A CKAN dataset is a collection of data resources (such as files or links to files), together with a description and other information that make the dataset discoverable. Datasets are what the users see when searching for the data.
This metadata describes the dataset you’re making available. It gives the person who might want to download it context about its collection and release, and if it will suit their purposes.
Essentially each dataset has:
- a title
- a detailed description of your dataset
- the download formats available
- the data owner (your agency)
- the open licence
Step 4: Creating a dataset is a two-step process.
-
Create dataset.
- Enter the data describing your dataset. This includes a title, URL, description and other metadata that is defined by the schema set out for the IAR.
- Enter the relevant data into the available fields.
- After all data is entered for the dataset, click the ‘Add Data’ button.
2. Add data.
Now you can add resources for each dataset. A resource can be any file or link to a file containing useful data in multiple formats.
This section includes a specific schema with relevant fields where data can be provided describing each data resource.
While the CKAN IAR is a catalogue of information about the datasets, it can host the dataset files themselves.
-
You have two options to provide the data to open data users:
- Provide the raw data - The dataset itself (stored on your servers), which means users can download the dataset from IAR.
- Provide a link to a data tool hosted outside of CKAN IAR.
-
Enter the data including name, descriptions, format, etc.
The format field describes the file formats being made available to the publicfor download. These can include formats like XML, Excel, CSV, etc.
-
After you have added all the data for a resource you can either ‘Finish’ or ‘Save & add another’ resource. One dataset can have multiple resources.
Step 5: After you finish adding the data and resources your dataset is added to CKAN IAR. You can continue to edit and, if necessary, transition through the relevant workflow.
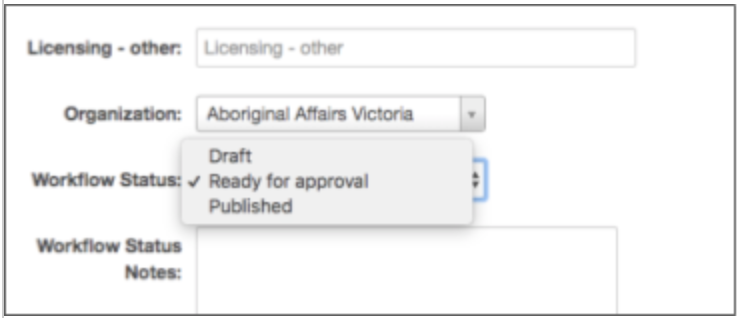
Dataset workflow
Creating a dataset includes the following publishing workflow:
Note:
-
Each dataset is initially created in a 'Draft' status.
-
A dataset’s status can be changed from 'Draft' to ‘Ready for Approval’.
-
A dataset’s status can be changed from ‘Ready for Approval’ to 'Published'.
-
A dataset’s status can be changed from ‘Ready for Approval’ to 'Draft'.
-
A dataset’s status can be changed from 'Published' to 'Draft'.
-
A dataset’s status can be changed from 'Published' to 'Archived'.
-
A dataset’s status can be changed from 'Archived' to 'Draft'.
A dataset that is in the 'Published' status is visible to all users within any organisation at a minimum.
Workflow notifications
As part of the publishing workflow logic, all datasets that are transitioned from the following status send out notification emails to the relevant organisation users:
-
'Draft' to ‘Ready for Approval’
-
'Published' to 'Draft'
The first transition above will trigger an email notification to admin users informing them that a dataset is ready for review with a link to the dataset. If an admin decides that the dataset is ready to be published then they can transition it from ‘Ready for Approval’ to 'Published' without any further action.
If an admin decides not to publish the dataset, they can revert back to ‘Draft’ and provide a reason to the dataset owner. An email notification will be sent to the owner and they can edit and make any changes as required before submitting back to ‘Ready for Approval’.
Dataset visibility
Another feature that can be set against a dataset is ‘Organisation Visibility’. This is done during the first steps of adding a new dataset or during editing of an existing dataset. This allows the editor and admin to decide who can see the dataset once it’s published. The options are:
Current -The dataset is only visible to users within the organisation that owns the dataset.
Parent -The dataset is only visible to users within the organisation that owns the dataset as well as shared up one level/step ONLY (for example from a Child/Grandchild Org up to the Parent/Child Org if relevant).
Child - The dataset is only visible to users within the organisation that owns the dataset as well as shared one level/step down ONLY to a Child/Grandchild org if relevant.
Family - The dataset is only visible to users within the organisation that owns the dataset as well as shared with all organisations up and down a structure, regardless of the number of levels/steps. This does not include sibling organisations.
All - The dataset is visible to users in any organisation
Organisation management
CKAN IAR organisations are used to create manage and publish collections of datasets. Organisations can include multiple levels of sub-organisations. Admin users can manage organisation setting and manage users within their organisation or any other organisation they are an admin in. Any admin user that creates a child sub-organisation of a parent organisation will inherently become an admin of the child organisation. Other admins, editors or members need to be added to sub-organisations to create/edit or access datasets that belong only to the sub-organisation. The dataset visibility logic described above allows admins to manage how a dataset becomes visible within the organisation structure (including sub-organisations) or across all organisations.
Data around Australia
Your data can be shared at your state data portal and on the federal repository at data.gov.au.
Get in touch
For more information on how to open your data contact us or reach out to your state data custodian. Use the form below or call us on 1300 727 952 to chat about your agency’s needs.